Better Cotton Launches Sustainability Roadmap in Uzbekistan
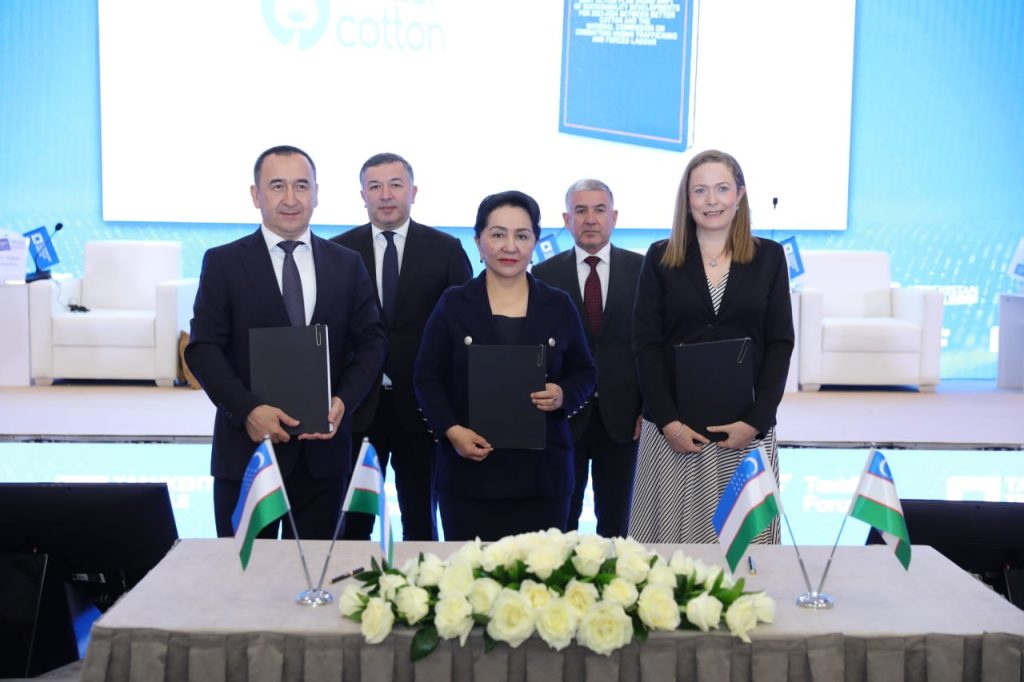


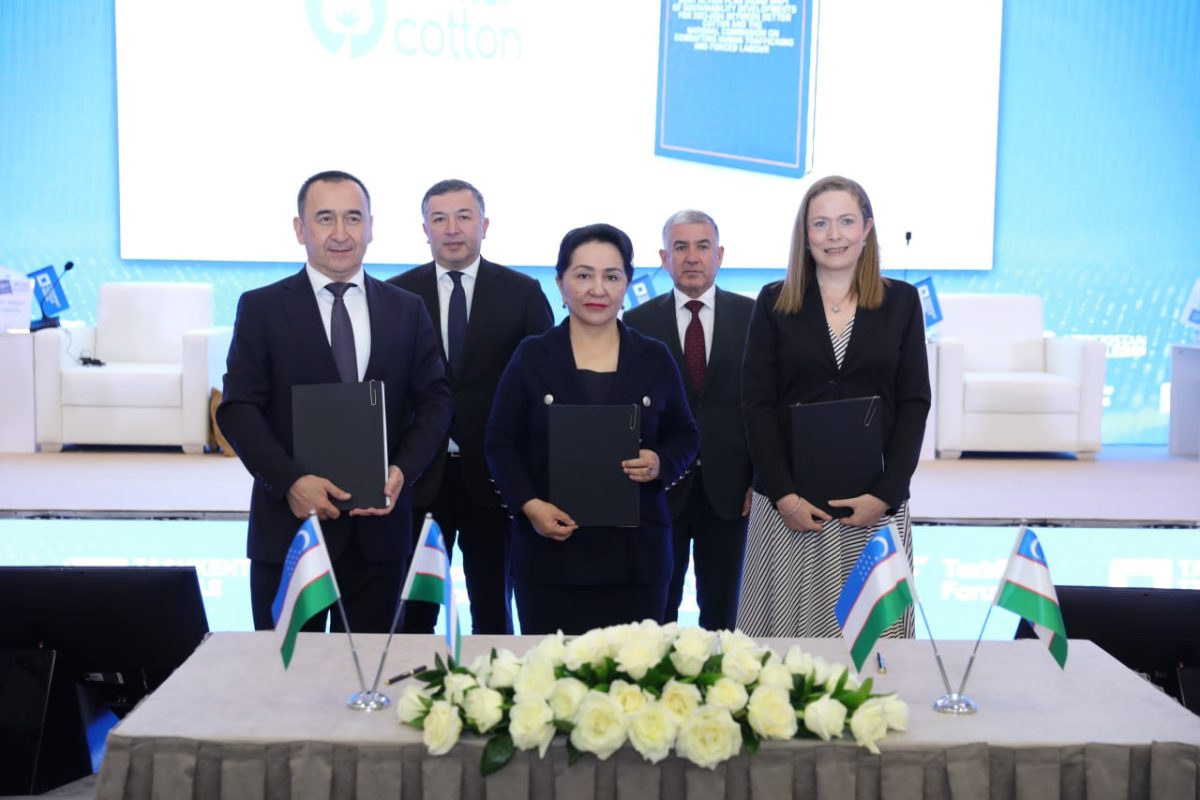
Better Cotton has developed and signed a Roadmap of Sustainability Developments with key stakeholders in Uzbekistan to drive further improvements in the country’s cotton sector.
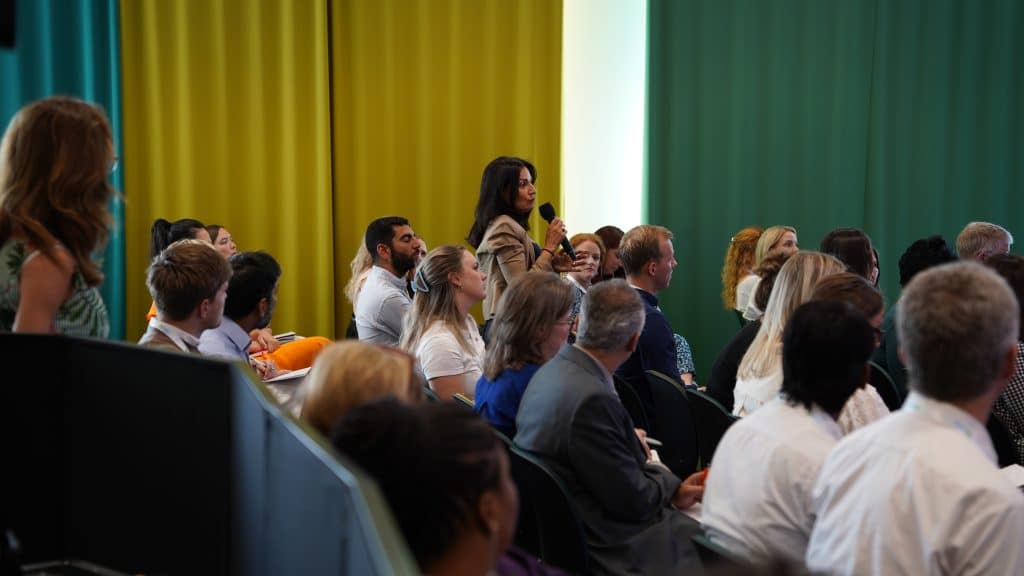
Uzbekistan’s Senate Chairperson and Chairperson of the National Commission to Combating Human Trafficking and Forced Labour, Her Excellency Tanzila Narbayeva, and Uzbekistan’s Textile and Garment Industry Association Chairperson, Mr. Ilkhom Khaydarov, were amongst signatories to the collaborative agreement during Tashkent Textile Week, from 29 May to 2 June.
At the event, Better Cotton’s Senior Programme Manager, Rachel Beckett, presented the roadmap to an audience of more than 600 delegates, including representatives from business, government, civil society, international organisations and educational institutes.
To advance the aims of the roadmap, national stakeholders have committed to supporting its implementation, including the Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Employment, and Textile and Garments Association, amongst others.
The roadmap will build on the Better Cotton Programme in Uzbekistan, launched in 2022. As the sixth largest cotton growing nation globally, operations in Uzbekistan are intrinsic to Better Cotton’s goals of mainstreaming more sustainable cotton production.
The roadmap effectively maps out a detailed action plan through which progress will be assessed in line with four overarching objectives.
The objectives are to:
- build effective management systems for the Better Cotton Programme in Uzbekistan and raise the awareness amongst cotton stakeholders in the country on sustainability pillars;
- promote the labour rights of workers in the cotton sector by putting in place effective labour systems that ensure decent work, safe and healthy working conditions, effective management of employer-worker relations as well as productive social dialogue;
- build key stakeholders’ awareness of best practices relating to environmental sustainability in cotton production and how these can be assessed at a field level;
- build a three-year strategy that defines the ways in which the Better Cotton programme can be managed, funded, and delivered at scale.
Better Cotton sees its work in Uzbekistan as an opportunity to create value and drive improvements for the environment, producers, and workers in the country’s cotton sector, and to bring us closer to our vision of a world where all cotton is more sustainable.
The roadmap’s approach will include recommendations by Better Cotton on how cotton growing communities across Uzbekistan can adopt more sustainable practices that are better for the environment, communities and the economy.
With the support of key Uzbekistan stakeholders, Better Cotton is well positioned to address any current and future concerns, and will strive to develop operations across the country to continually support cotton farmers.
We believe that our partnership with Better Cotton will support the creation of effective management systems in cotton fields, encourage the broader application of modern, energy-saving technologies and reduce the impact of production on the environment. This roadmap serves to strengthen social protection, improve labour relations based on international standards, and create decent and safe working conditions for workers.