COP28: Better Cotton’s Conference Takeaways


In late November, ahead of her trip to Dubai to represent Better Cotton at the 28th session of the UN Climate Change Conference of Parties (COP28), we spoke to Public Affairs Manager Lisa Ventura about our plans and objectives at the climate conference.
Now that COP28 has drawn to a close, we caught up again with Lisa to hear about her experience at the conference, the progress made, and her key takeaways.
What are your reflections on COP28?


For the first time, agriculture was a major focus at this year’s summit, with a full thematic day on 10 December. Given the contribution of agriculture to global emissions, this was a big step forward to finding solutions to climate change in a meaningful way.
Governments called for the implementation of multi-sectoral solutions on climate and agriculture, such as land use management, sustainable agriculture, resilient food systems, nature-based solutions and ecosystem-based approaches. Most importantly, they recognised that these innovative and sustainable agricultural practices create economic, social and environmental benefits, improved resilience and well-being in particular.
However, it is important to remain attentive to the focus given to food systems when COP and other climate discussions address agricultural topics. The active participation of organisations like Better Cotton is key to ensuring a balanced and integrated approach that takes into consideration all crops.
After a lot of back and forth, there is finally an agreement to transition ‘away from fossil fuels in energy systems, in a just, orderly and equitable manner’ to avert the worst effects of climate change. This transition from fossil fuels will impact every supply chain.
I’d also like to emphasise just how important COP has become for the sustainability ecosystem. All actors who wish to play their role in the future of our economic, social and environmental frameworks were present, and the Conference is driving the international agenda as a whole.
How will the UN climate negotiations at COP28 affect cotton farming and farmers around the world?
Farming communities around the world are already facing adverse impacts of climate change. Following droughts, crop yields are expected to fall significantly, resulting in diminished crop yields and overall livelihoods, and the recent floods in Pakistan and crop pests in India are just two of the recent examples of the issues impacting cotton farming.
Nevertheless, we must also bear in mind that cotton farming produces greenhouse gas emissions and that negotiations at COP are spearheading changes in agricultural systems towards more resilient and sustainable practices.
At COP28, delegates agreed to operationalise the Loss and Damage Fund, established last year at COP27, which aims to support especially vulnerable countries dealing with the effects of climate change. The decision taken in Dubai means that countries can start to pledge resources to it. This is a great starting point for the international community to find concrete means to support the livelihoods of many people, including farmers.
How did Better Cotton contribute to COP28, and what will you take forward from the conference?
Firstly, I feel a sense of pride that Better Cotton has been admitted to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) as an observer organisation. This means we can attend all future sessions of COP, take part in the negotiation processes and play an important role in the global efforts to combat climate change. It also reflects Better Cotton’s role in promoting sustainable development within the international community.
Climate change can only be addressed if is it addressed holistically. To that end, we shared our climate change approach across various sessions and throughout our engagement, as it is key for cotton farming to be seen as part of the solution. For example, we hosted a side-event on how to drive the adoption of climate-smart practices in global value chains.
From the speakers of this session to farmers I met at the conference (kudos to our colleagues at Fairtrade for facilitating the participation of a delegation of farmers), climate finance was brought up time and again as the biggest gap to scale those existing tools. Greater access to resources is the only way to truly enable climate resilience and enhance smallholder livelihoods while enabling a transition to farming systems that produce sustainable crops.
We have demonstrated our commitment to inclusive collaboration and transparency by signing the United Nations’ International Trade Centre’s (ITC) ambitious ‘Uniting Sustainable Actions’ initiative, which champions the work of small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in global supply chains.
Carbon markets were also at the heart of many discussions, but government representatives did not reach an agreement on carbon trading rules (Article 6 of the Paris Agreement). As Better Cotton is developing its own GHG accounting system, it was important for us to understand how international carbon market mechanisms are being developed.
Finally, considering the significant percentage of emissions emitted by the fashion industry, I was surprised not to see more stakeholders representing this industry. There were, of course, some discussions about decarbonisation of the supply chains, but it remained on the sidelines. Greater focus on this sector is needed at COP to turn ambitious commitments from retailers and brands into legislation and measurable progress.
Going forward, we already have many ideas on how to contribute to future COPs, and are already discussing new partnerships to mobilise stakeholders in the cotton industry during these important events.
Read moreCelebrating World Cotton Day 2023


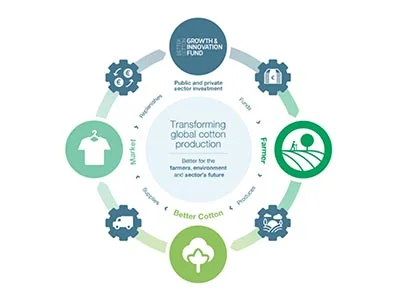
Today we celebrate World Cotton Day 2023, an annual commemoration of one of the world’s most renewable resources and a commodity that supports approximately 100 million families.
At Better Cotton, we’re working every day to support and strengthen cotton growing communities so they can keep growing the crop they rely on. As the world’s largest cotton sustainability initiative, our strategic aims are to embed sustainable farming practices and policies; enhance well-being and economic development; and drive global demand for sustainable cotton. We believe in the power of sustainable cotton to transform livelihoods and the environment.
World Cotton Day was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 2021. The annual date is 7 October, but this year is being celebrated on 4 October with a World Cotton Day 2023 event hosted by the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) in Vienna, Austria.
This year’s theme is “Making cotton fair and sustainable for all, from farm to fashion.”
We’re proud to have our own Jacky Broomhead, Senior Traceability Manager, presenting at WCD 2023. She’s discussing ‘Traceability as an innovation for the cotton sector’ – a topic we’ve been focusing on as we prepare to launch our Traceability Solution next month and continue to explore how we can create more opportunity for farmers and the rest of the sector.
We’ve also this week had CEO Alan McClay speak at The Economist’s Sustainability Week in London, participating in a panel called ‘Word on the High Street – Making Fashion and Cosmetics Sustainable.’
This is a movement and not a moment, and we hope everyone – brands and retailers, manufacturers, producers and consumers – will join us and be part of something better.

Better Cotton Impact Targets: Q&A with Nisha Onta, Regional Coordinator for Asia at WOCAN




Millions of women around the world dedicate their lives to cotton production, and yet their representation and contributions aren’t fairly reflected within the sector’s hierarchies.
It’s with this in mind that Better Cotton recently launched its 2030 Impact Target for Women’s Empowerment. Over the coming years, we aim to reach one million women in cotton with programmes and resources that promote equal farm decision-making, build climate resilience, or support improved livelihoods. What’s more, we commit to ensuring that 25% of field staff are women with the power to influence sustainable cotton production.
To achieve this, we’ll collaborate closely with leading organisations to create the environment for field-level change. Here, we speak to Nisha Onta, Regional Coordinator for Asia at WOCAN, to understand the topic’s complexities and obstacles preventing women from advancing their careers in cotton. Nisha is amongst four keynote speakers at this year’s Better Cotton Conference, taking place in Amsterdam from June 21.
Historically, what have been the barriers to access to training for women in sectors such as cotton farming?
There are a lot of research findings which show that the major barrier for women to access training are time poverty, access to information and restrictions on mobility.
Time poverty simply means there is just not enough free time in the lives of women to add more training to their schedule. It is called the ‘triple burden’ of women. Women are responsible for productive, reproduction and communal roles. Therefore, in order to make sure we want to invite more women to train, organisers will have to provide childcare facilities, the timing of the training has to be reasonable for them and the training should address the triple burden so it is not adding to their already packed schedule of responsibilities.
Access to information is also critical, there are many instances that women are simply not aware of the availability of training or resources. Therefore, the usual mode of communication, such as sending training schedules to local representatives and news in the media might not reach the women we are trying to train. Perhaps using local women cooperatives and other mediums that are accessible to women could increase their participation.
Mobility issues can be due to cultural issues or simply the issue of infrastructure. If the training is scheduled for the evening but local safe transport is not available, for example. In some communities, women may not be allowed to travel to participate in trainings, then the organisers will have to use different strategies to convince the head of the households to give permission for the women to attend.
How influential will the provision of training for women be to increasing their representation in decision-making roles?
Ensuring that there’s capacity for women to participate in decision-making is critical to increasing their representation. If the system is not designed to include women in leadership positions, no matter how much training is available, they’ll never have equal opportunities. Therefore, a systematic rethink is required to create the space for women to participate and influence the cotton sector they contribute so much to.
How important will support from organisations like Better Cotton be to enabling this shift within the sector?
Organisations like Better Cotton can be catalysts to advance gender equality in the cotton sector. Better Cotton’s vast network touches millions of farmers around the world and this infrastructure will be important to driving changes at the field-level. Better Cotton’s Women’s Empowerment Impact Target will serve an important purpose to the sector if we’re to see women afforded the chances that have historically been set aside for men.
By 2030, what infrastructural changes would you like to see within agriculture to better support women?
There needs to be the space for women to voice their opinion and influence the sector’s development through decision-making positions. There has to be more direct resources such as trainings, credit and grants for women led business. These changes will inspire and impact future generations across agriculture and may also encourage the creation of more women-led businesses in the cotton value chain.
Read moreBetter Cotton Impact Targets: Q&A with Tamar Hoek, Better Cotton Council Member and Solidaridad’s Senior Policy Director for Sustainable Fashion




Ninety-nine percent of the world’s cotton farmers are smallholders. And whilst production capacities per farmer may be small, together, they represent the bedrock of an entire industry, enabling its global reach.
With the launch of our recent 2030 Impact Target to promote Sustainable Livelihoods, we’re committed to increasing the net income and resilience of two million cotton farmers and workers.
It’s a bold ambition and one we won’t be able to reach without the support of a vast network of partners. In this Q&A, we hear from Better Cotton Council member and Solidaridad’s Senior Policy Director for Sustainable Fashion, Tamar Hoek, about the complexity of this topic and the role Better Cotton can play in supporting smallholders.
In supporting the development of Better Cotton’s Smallholder Livelihoods Impact Target, what issues were you and Solidaridad most keen to see the organisation address and how do you think its target will contribute to achieving this?
We are glad that Better Cotton decided to include net income and resilience for farmers as one of its targets. The livelihoods of farmers and farm workers depend on the price that is paid for the cotton but also on how capable the farmer is of dealing with uncertainties in production. For Solidaridad, the topic of living income has been high on our agenda for years. With the scale that Better Cotton brings, this new target can potentially lead to a higher income for a lot of farmers around the world, which is the first step towards a living income. The target will hopefully lead to appropriate tools for increasing net income, greater awareness in the value chain, best practices and income benchmarks that are needed to eventually scale the improvements.
With the scale that Better Cotton brings, this new target can potentially lead to a higher income for a lot of farmers around the world, which is the first step towards a living income.
What influence would increasing cotton farmers’ net income have on their ability to promote more sustainable agricultural practices and react to shocks and stressors in the market and the environment?
First of all, increasing a net income should give the farmer the opportunity to improve their livelihood, the situation of his/her family and to save for unexpected situations. Then, improvements can allow for payment of better wages and working conditions, the purchase of health and safety equipment, and perhaps investment into more sustainable pesticides and fertilisers. We all know that the price that is paid for cotton is not enough for all of these investments, both socially and environmentally. Therefore, the increase of the price – and with that the net income – is a start that will allow for a lot of improvements that are needed for more sustainable production. (Editor’s note: While Better Cotton strives for the collective improvement of sustainable livelihoods, our programmes have no direct influence over pricing or commercial activities)
Given Better Cotton’s global reach, can you discuss the potential for its Impact Target to address structural poverty which persists in the sector?
Hopefully, Better Cotton will join forces with other organisations in the industry to scale the impact of the target and collectively come to a living income demand for all cotton farmers in the world. Better Cotton will need to lobby with policymakers, local governments and other stakeholders in the value chain to make sure that the right enabling environment is in place to get rid of systemic issues. Addressing structural poverty is ambitious but that will not happen overnight with just raising the net income of a group of farmers and looking at their resilience. It eventually needs a whole value chain to change and, for that, Better Cotton needs to work collaboratively.
Read moreBetter Cotton Announces myBetterCotton, New Member Portal Launching in 2023


Better Cotton today announces that it will be launching myBetterCotton, a new portal for Better Cotton Members, later this year. Access to the portal will be granted to Members in a phased rollout, starting mid-2023 and continuing throughout the rest of the year.
The myBetterCotton portal has been created in order to improve the Better Cotton membership experience, taking into account the responses from our 2022 Member Feedback Survey. The new portal will provide a platform for Members to connect, collaborate and network, whilst making it easier for them to engage with Better Cotton.
The myBetterCotton portal is built around four key areas:
- ‘My Membership’ – empowering Members to take control of their organisation’s information and keep it updated, this section will map out the onboarding process and allow Members to review and manage open or pending actions.
- ‘My Community’ – a space for Members to engage, collaborate and network online. Direct chat and discussion group features will offer Members the opportunity to share opinions, discuss news and talk about their successes and challenges with one another. Members will also be able to view events and webinars and register to attend.
- ‘My Sourcing’ – where Retailer and Brand Members can explore sourcing guidance, submit their cotton consumption and review their goals, and keep up to date with their progress towards meeting targets.
- ‘My Claims’ – allowing Members to explore claims guidance and facilitate submissions of marketing and communications materials for review. Members will be able to review any claims they submitted previously.
myBetterCotton is our new and exciting meeting place for Members to network and learn more about Better Cotton. Our vision is that it will help newcomers to Better Cotton blossom into seasoned Members who promote Better Cotton and believe in our mission to improve farmer livelihoods and the environment. We will share regular updates and moderate your insightful discussions and look forward to welcoming you online over the course of 2023.
Members will receive more information about myBetterCotton, including when they can expect to receive access to the portal, by email in the coming months.
Read moreWhat’s in Store For the Rest of 2023?


By Alan McClay, CEO of Better Cotton


Better Cotton made significant strides in 2022 towards our vision of a world where more sustainable cotton is the norm. From the unveiling of our new and improved reporting model to a record 410 new members joining in one year, we prioritised on-the-ground change and data-driven solutions. The development of our traceability system entered a new phase with the stage set for pilots to commence, and we secured funding of over 1 million EUR to continue our work for traceable Better Cotton.
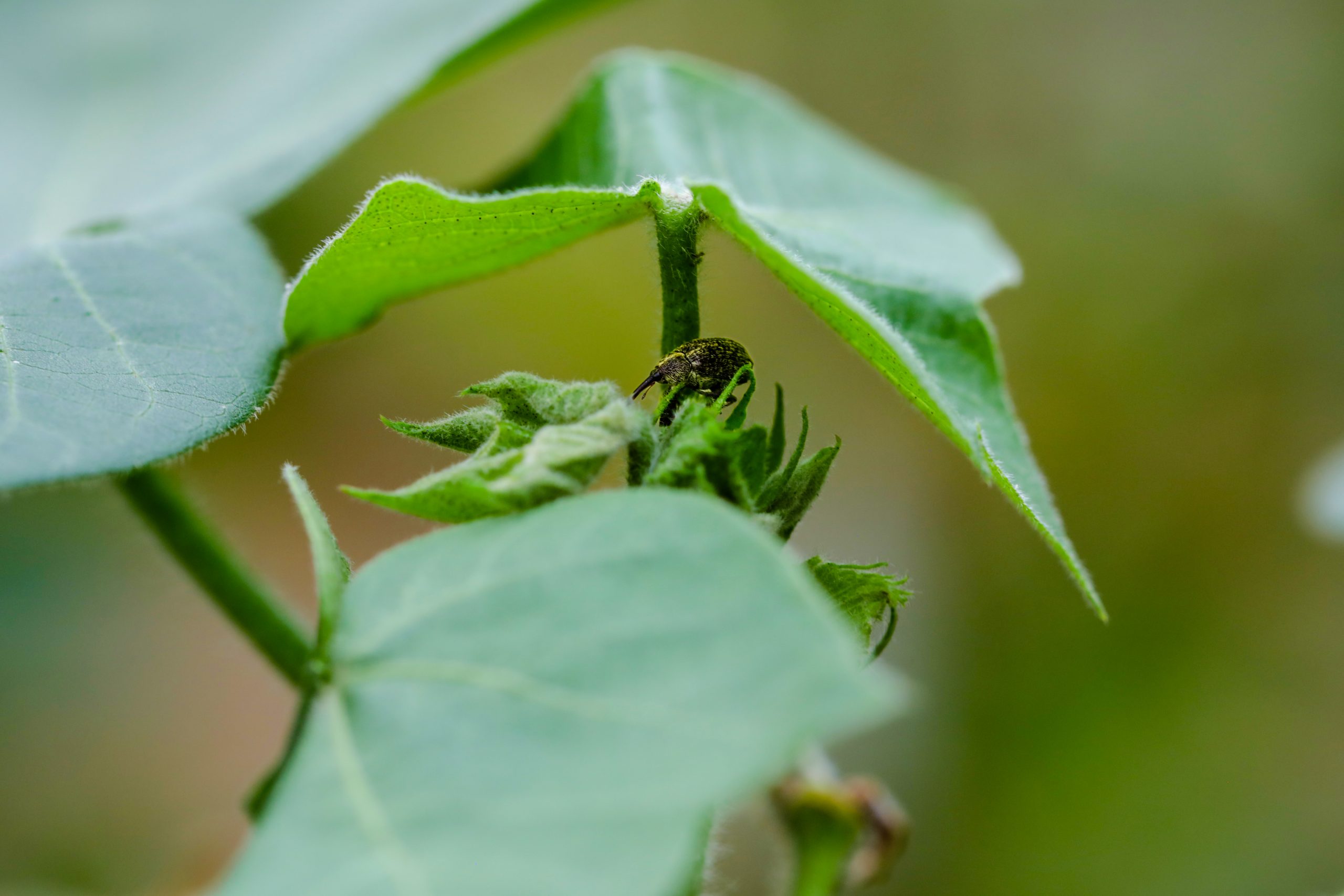
We have continued this momentum into 2023, kicking the year off with our Programme Partner Meeting in Phuket, Thailand under the twin themes of climate change and smallholder livelihoods. Our commitment to knowledge sharing continued as we collaborated with ABRAPA, the Brazilian Association of Cotton Producers, to organise an Integrated Pest Management workshop in Brazil in February, with the aim of sharing research and innovative initiatives regarding the control of pests and diseases in the cotton crop. We are committed to supporting all efforts to reduce pesticide use.
As we approach the end of the first quarter of 2023, we’ve been taking stock of the current sustainability landscape and mapping out how we can best use our resources and expertise at Better Cotton to address the challenges and opportunities on the horizon.
Welcoming a new wave of industry regulation and introducing Better Cotton traceability
2023 is an important year for sustainability as a growing set of regulations and legislation are being implemented around the world. From the EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles to the European Commission’s initiative on substantiating green claims, consumers and lawmakers have wised up to ambiguous sustainability claims like ‘zero emissions’ or ‘eco-friendly’ and are taking steps to make sure claims are verified. At Better Cotton, we welcome any legislation that supports a green and just transition and recognises all progress on impact including at field level.
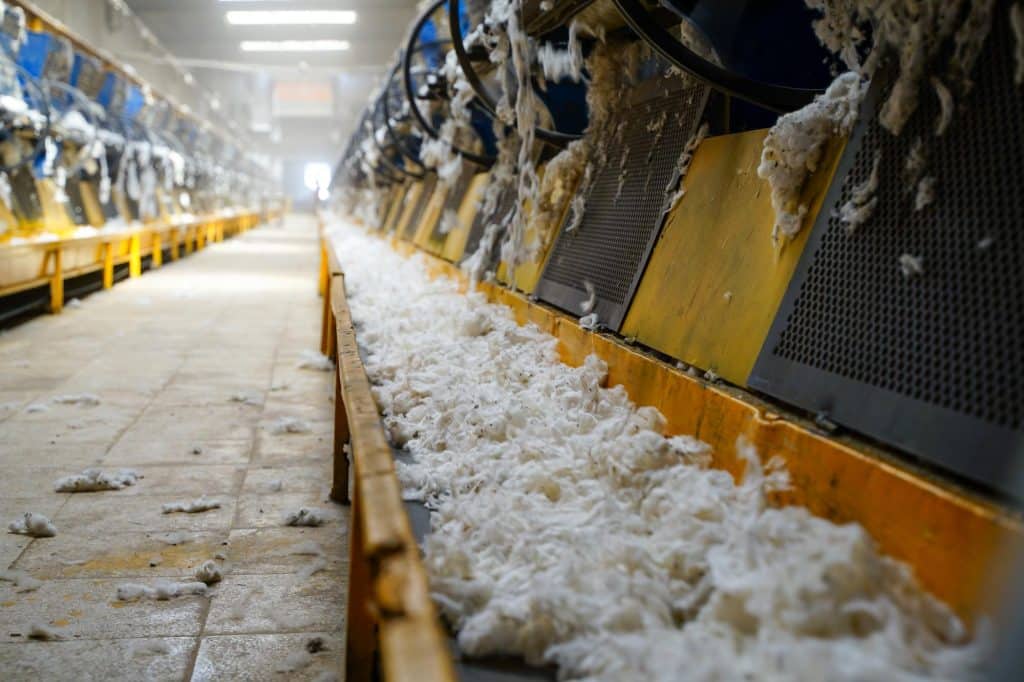


In late-2023, following our supply chain mapping efforts, we will begin to roll out Better Cotton’s global traceability system. The system includes three new Chain of Custody models to physically track Better Cotton, an enhanced digital platform to record these movements, and a new claims framework which will give members access to a new Better Cotton ‘content mark’ for their products.
Our commitment to traceability will ensure Better Cotton Farmers, and particularly smallholders, can continue to access increasingly regulated markets, and we will drive significant growth in the volume of traceable Better Cotton. Over the coming years, we plan to create additional benefits for Better Cotton Farmers including local investment by providing direct connections with retailers, brands, and customers.
Optimising our approach and launching the remaining Better Cotton Impact Targets
In line with growing calls for evidence on sustainability claims, the European Commission has also issued new rules on corporate sustainability reporting. Most notably, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive came into force on 5 January 2023. This new directive introduces stronger reporting rules for companies operating in the EU and pushes for greater standardisation in reporting methodologies.
After more than 18 months of work, we announced a new and improved approach to our external reporting model at the end of 2022. This new model tracks progress over a multi-year timeframe and integrates new farm performance indicators aligned with the Delta Framework. In 2023, we will continue to share updates on this new approach in our Data & Impact blog series.
During the first half of 2023, we will also be launching the remaining four Impact Targets connected to our 2030 Strategy, focused onpesticide use (as mentioned above), women’s empowerment, soil health and smallholder livelihoods. These four new Impact Targets join our climate change mitigation target to complete our plan to make cotton better for the farmers who produce it and for all those who have a stake in the future of the sector, as well as for the environment. These progressive new metrics will allow better measurement and drive change across five key areas to ensure greater lasting economic, environmental and social benefits at the farm level for cotton-growing communities.
Unveiling our new Better Cotton Principles and Criteria
For the last two years, we have been revising the Better Cotton Principles and Criteria, which lay out the global definition of Better Cotton. As part of this revision, we are going further to integrate key components of regenerative agriculture, including core regenerative practices such as maximising crop diversity and soil cover while minimising soil disturbance, as well as adding a new principle on improving livelihoods.
We are nearing the end of our review process; on 7 February 2023, the draft P&C v.3.0 was officially approved for adoption by the Better Cotton Council. The new and improved Principles and Criteria are expected to be launched in the first half of 2023, followed by a transition year, and will come into full effect in the 2024-25 cotton season.
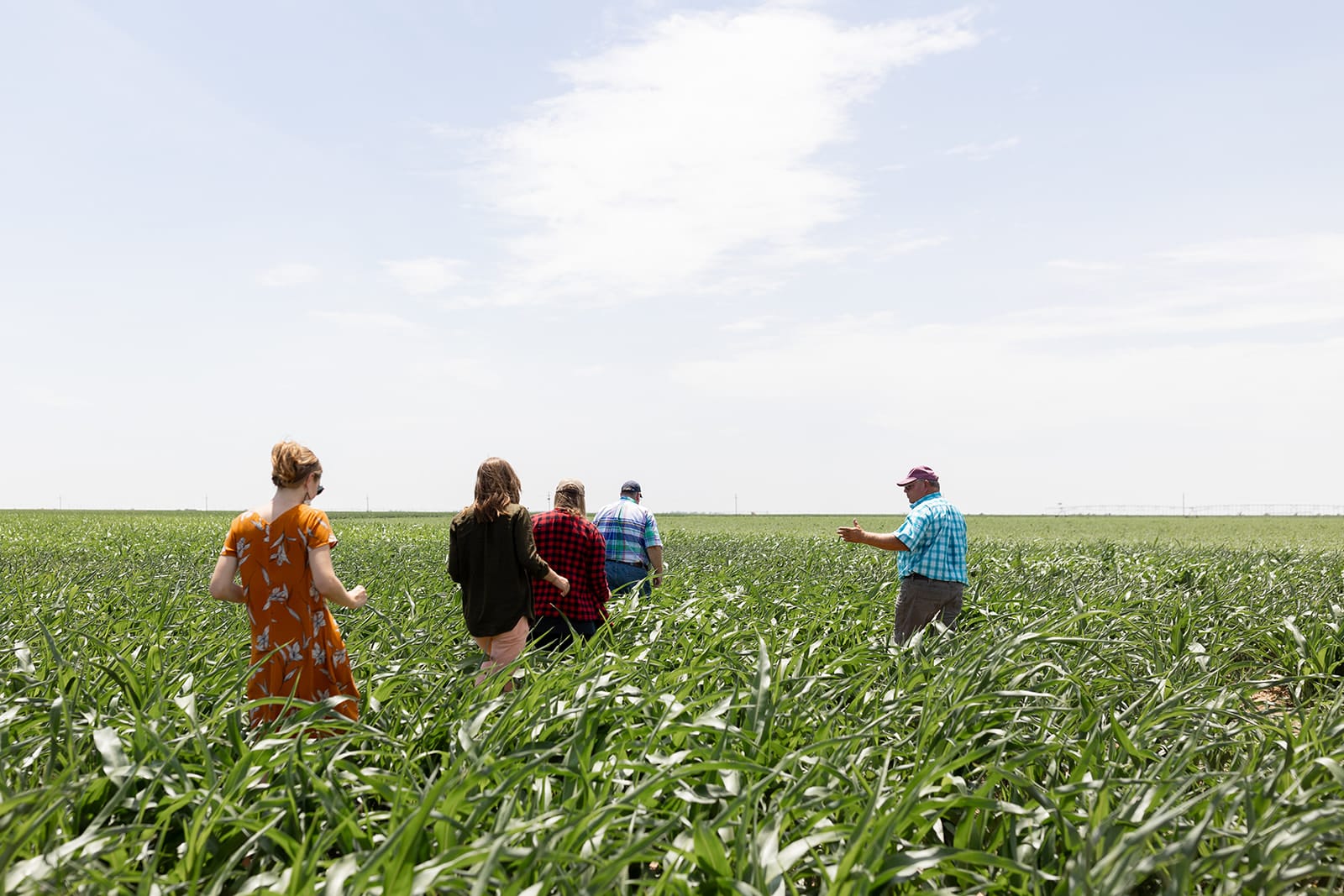
See you at the 2023 Better Cotton Conference
Last but not least, in 2023 we are looking forward to once again convening industry stakeholders at the 2023 Better Cotton Conference. This year’s conference will take place in Amsterdam (and virtually) on 21 and 22 June, exploring the most salient issues and opportunities in sustainable cotton production, building on some of the topics which we’ve discussed above. We are excited to gather our community and welcome as many of our stakeholders as possible at the conference. We hope to see you there.
Read moreQ&A: Dr Peter Ellsworth and Dr Paul Grundy on Integrated Pest Management
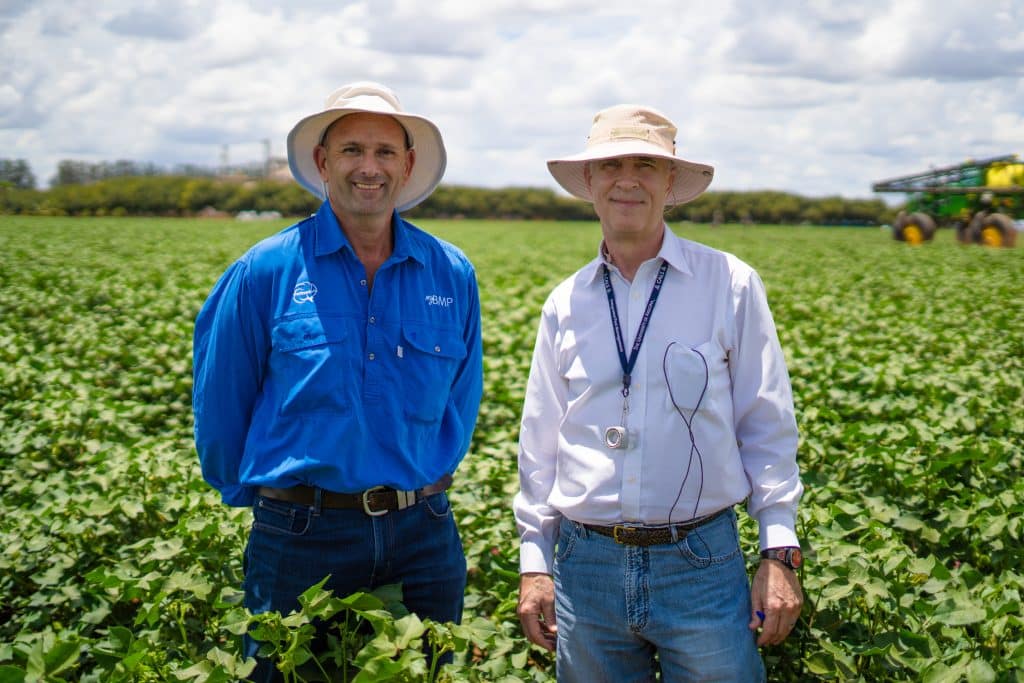


From 28 February to 2 March 2023, Better Cotton held a workshop in collaboration with ABRAPA, the Brazilian Association of Cotton Producers on Integrated Pest Management (IPM). IPM is an ecosystem approach to crop protection that combines different management practices into a strategy for growing healthy crops.
Taking place in Brasilia, the workshop brought together a range of international experts, with presentations and discussions on the latest research and best practices. It also included a field trip to a farm to look at the different ways pest management is executed on a large-scale farming system, including both the successes and challenges.
During the workshop, we sat down with Dr Peter Ellsworth, Professor of Entomology and Extension IPM Specialist at the University of Arizona and Dr Paul Grundy, Technical Lead for IPM at CottonInfo in Australia to talk about their experiences and expertise in IPM.
Let’s start with some definitions – can you explain to me what a biopesticide is?
Dr Peter Ellsworth: In terms of what most people think, it just means a biologically derived pesticide. A pesticide is just something that kills a pest. What a lot of people don’t understand is that a pest is only an organism out of place or out of time. So that could be a weed, it could be a virus, a bacterium, an insect or a mite.
Dr Paul Grundy: I’d describe it as a pathogenic organism that you can spray for the control of a pest. It will be either a virus, fungus or a bacterium. A key advantage is that many biopesticides have a narrow target range and can work well within an IPM program.
What about beneficials, natural enemies and cultural controls?
Dr Peter Ellsworth: When it comes to natural enemies and beneficials, there’s a little nuance there. A natural enemy would be usually some arthropod that feeds on other arthropods, but it could include the pathogens that naturally kill our insects. A beneficial includes all natural enemies, but also includes our pollinators and other organisms that have value in our system.
Dr Paul Grundy: Cultural controls are a range of things. It could be something as simple as an agreed sowing or crop end date. Essentially, it can be anything that entails a crop management tactic that disadvantages a pest.
Peter, can you explain the Arizona scouting and monitoring method that you developed?
Dr Peter Ellsworth: Sure – it’s just counting! But it’s about knowing where to count. In the case of Bemisia whiteflies, you have an animal that can colonise any part of the plant. It can be anywhere on any of the hundreds of leaves on the plant. So, years ago, we did studies to figure out exactly which leaf is most representative of the overall distribution of whitefly adults on the plant. Then we did the same thing for the eggs and nymphs.
Basically, the method is about counting down to the fifth leaf from the top of the plant, turning it over, and when there are three or more adult whiteflies on this leaf, classifying it as ‘infested.’ You also count large nymphs – you detach the leaf, turn it over and you look at a disc the size of a US quarter, using magnifying loupes that we have outfitted with a properly sized template, and if there’s one nymph in that area it’s infested. You tally these two counts up, and when you have a certain number of infested leaves and infested leaf discs, you know if it’s time to spray.
You’re from Australia and the US, which mainly have large cotton farms – but when it comes to Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for smallholders, how much is transferable?
Dr Paul Grundy: Conceptually, it’s the same thing. Pest management is a people business, so the principles for IPM are just as applicable on a small scale as they are on a large scale. There are obviously different logistical scales associated, but the principles are very similar.
Dr Peter Ellsworth: Yeah, the principles I would say are identical. But there are a couple of notable things that change what a smallholder can do. One of them is area-wide factors. Unless the smallholder is terribly well connected with their community and many, many other smallholders cooperate, they don’t have the ecological landscape engineering opportunities that Mato Grosso has. Large farms can do very specific things around isolation, crop placement and timing and sequencing that a smallholder just wouldn’t be able to take advantage of. These area-wide approaches represent important prevention or avoidance tactics that reduce pest pressures on your cotton crop.
The other thing is the hazards. It depends on the smallholder, but for the most part, some of the safety procedures and equipment aren’t necessarily available there, so the stakes are so much higher.
What’s more important in IPM, people or technology – and how do you think about data and its importance in IPM?
Dr Peter Ellsworth: There’s no reason for IPM without people because we define what a pest is. I always say no bug was born to be bad, we make it bad. We place value on specific things in our world, whether that’s agricultural production, or having a mosquito-free home, or running a non-rat-infested restaurant.
Dr Paul Grundy: From a technology and research perspective, we use data to understand and describe what’s going on and to determine whether what we’re putting in place is successful or otherwise. So, if we look at pesticide use data and then we look at pest resistance testing data, often you can match those to data sets up to understand on-farm changes. Typically, a change in resistance will more than reflect a change in chemical use patterns, which is why it’s important to have that on-farm data. We have a saying in Australia which is “If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it”.
How important is international collaboration in IPM?
Dr Paul Grundy: I’ve learned a lot from international collaboration. For example, in preparation for the possibility that Begomoviruses might enter Australia following the spread of its vector, the silver leaf whitefly in the mid-2000’s, we assembled a team that went to Pakistan to learn what we could from those with experience and form connections with people who we would be able to talk to should this problem emerge in Australia. That since came around full circle through Better Cotton – with my subsequent involvement with Pakistan researchers who have wanted to learn from us how to better implement IPM. The exchange of information is always valuable in both directions.
Dr Peter Ellsworth: I’ve worked a lot in northern Mexico. Sometimes people say, “You’re in US cotton, why are you helping Mexican growers?” I say that they’re our neighbours and any problem they have could be ours. They jointly eradicated boll weevil and pink bollworm with us, for example. They’re important partners in business and in everything.
Some people asked the same question about why I’m coming to Brazil, but I don’t look at the cotton industry in terms of competitors. I do think as an industry worldwide, there are many more ties that bind than separate.